- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial in managing this prevalent and often disruptive condition.
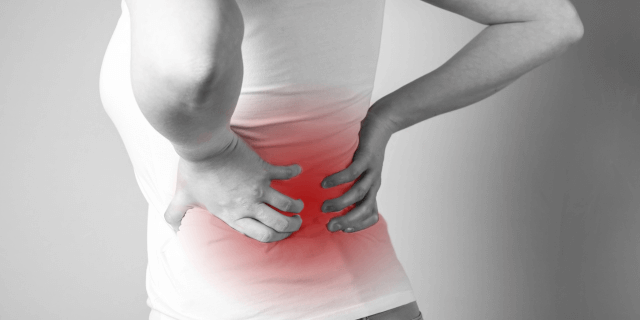
Lumbago, commonly known as lower back pain, is a prevalent medical condition affecting millions worldwide.
It can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain, often hindering daily activities and significantly impacting the quality of life.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial in managing this prevalent and often disruptive condition.
Causes and Symptoms
Various factors, including muscle strains, ligament sprains, herniated discs, or underlying health conditions, can cause low back pain. Common causes include improper lifting, poor posture, lack of regular exercise, fractures, ruptured discs, or arthritis.
Additionally, overuse, such as working out or lifting too much, prolonged sitting or laying down, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, and wearing a poorly fitting backpack can contribute to lower back pain.
Signs and symptoms of lumbago can range from a dull ache to a stabbing or shooting sensation. The pain may make it hard to move or stand, and stiffness and posture problems are common. Sometimes, the pain occurs after a specific event, while other times, the cause may be unknown.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing lumbago typically involves a physical examination and imaging studies. Imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans can provide clear pictures of the vertebrae, discs, muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
Electromyography (EMG) may be conducted to test nerves and muscles, while blood and urine tests can also aid in diagnosing lumbago.
Treatment Options
Treatment for lower back pain usually begins with rest and pain relievers. However, the specific treatment approach depends on the underlying cause. Medication, physical therapy, injections, and surgeries may be recommended in some instances.
Maintaining a healthy weight and strengthening abdominal muscles can also help prevent lower back pain.




-1770826318-md.jpg)




-1770826318-sm.jpg)