- Addressing this urgent situation requires a multifaceted approach that combines various strategies.
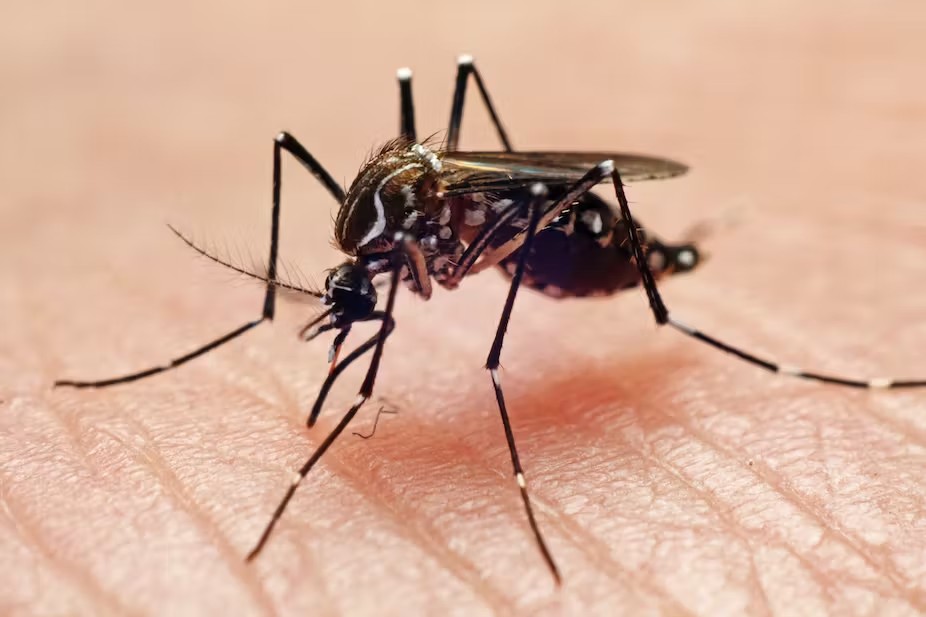
The presence of deadly mosquitoes in Kenya, including species such as Anopheles mosquitoes transmitting malaria and Aedes mosquitoes spreading diseases like dengue and Zika, poses a significant threat to public health.
Addressing this urgent situation requires a multifaceted approach that combines various strategies.
By investing in mosquito control measures, raising public awareness, leveraging technology for early detection, and strengthening healthcare infrastructure, Kenya can effectively combat these deadly mosquitoes and protect its population from the devastating impact of mosquito-borne diseases.
One of the critical pillars in combating deadly mosquitoes is investing in widespread mosquito control measures. This includes the distribution of insecticide-treated bed nets, which have proven highly effective in reducing malaria transmission.
Indoor residual spraying is another crucial method that involves treating the walls and surfaces of homes with insecticides to kill mosquitoes.
Read More
Larval source management, which targets mosquito breeding sites to prevent larvae development, can significantly contribute to reducing mosquito populations.
By implementing these control measures on a large scale, Kenya can create a formidable defence against mosquito-borne diseases.
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in preventing mosquito-borne diseases. Educating communities about the importance of preventive measures is crucial.
Emphasizing insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and practising good hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of mosquito bites.
These campaigns should also promote the proper use and maintenance of bed nets and highlight the importance of seeking medical attention promptly when symptoms arise.
By empowering individuals with knowledge, Kenya can enable communities to participate actively in disease prevention and control efforts.
Utilizing technology for early detection and monitoring of mosquito-borne diseases can greatly enhance response capabilities.
Implementing surveillance systems that track mosquito populations, disease prevalence, and geographical distribution can provide valuable insights for targeted interventions.
Additionally, mobile applications and remote sensing technologies can assist in collecting data and mapping mosquito breeding sites.
By harnessing the power of technology, Kenya can proactively identify areas at higher risk and implement timely interventions to prevent outbreaks.
A robust healthcare infrastructure is crucial for effective management of mosquito-borne diseases. This includes ensuring access to diagnostic tools and quality healthcare services for timely diagnosis and treatment. Training healthcare professionals to identify and manage mosquito-borne conditions is essential.
Strengthening laboratory capacities for accurate diagnosis and surveillance enhances the ability to respond swiftly. By prioritizing investments in healthcare infrastructure, Kenya can improve the detection and management of mosquito-borne diseases, ultimately saving lives.
Addressing the challenge of deadly mosquitoes requires collaborative efforts from various stakeholders. Governments, healthcare providers, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and communities must work together to develop a comprehensive and sustainable strategy.
This involves sharing resources, expertise, and knowledge to implement effective control measures, conduct research, and raise awareness.
Engaging communities and involving them in decision-making ensures interventions' ownership and sustainability. By fostering collaboration, Kenya can build a resilient defence against deadly mosquitoes and protect the health and well-being of its population.